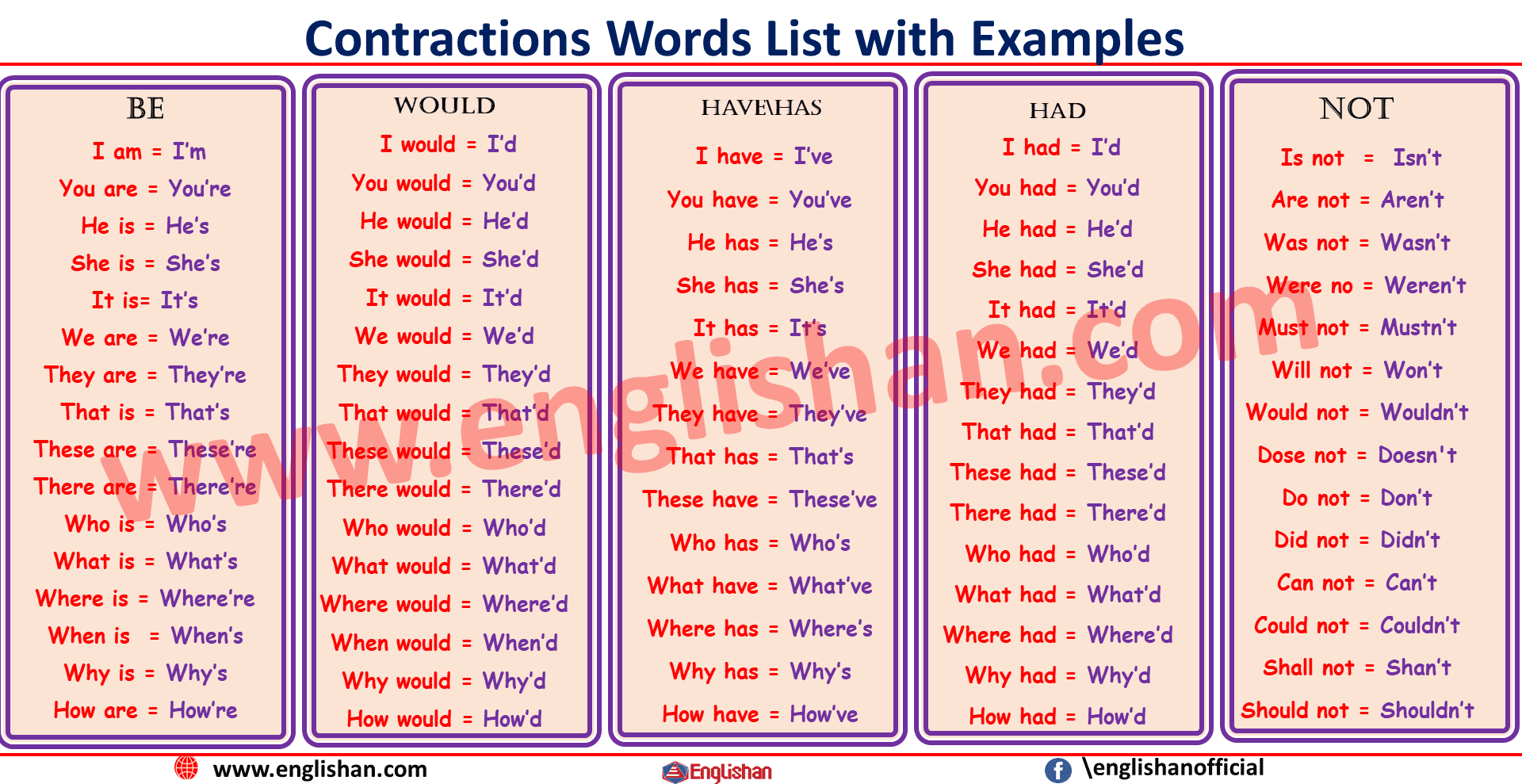
Contractions are shortened forms of words that are commonly used in English. They are created by combining two words and removing some letters and replacing them with an apostrophe. Contractions are widely used in spoken English, informal writing, and messaging. They make communication more natural and fluent, and they help speakers and writers to convey their messages more effectively. In this article, we will explore the usage of contractions in English and how they affect communication.
Contractions
We also use an apostrophe to shorten or contract two words together.





|
Be |
|
|
I |
I am = I’m |
|
You |
You are = You’re |
|
He |
He is = He’s |
|
She |
She is = She’s |
|
It |
It is= It’s |
|
We |
We are = We’re |
|
They |
They are = They’re |
|
That |
That is = That’s |
|
These |
These are = These’re |
|
There |
There are = There’re |
|
Who |
Who is = Who’s |
|
What |
What is = What’s |
|
Where |
Where is = Where’re |
|
When |
When is = When’s |
|
Why |
Why is = Why’s |
|
How |
How are = How’re |
would contractions list
|
Would |
|
|
I |
I would = I’d |
|
You |
You would = You’d |
|
He |
He would = He’d |
|
She |
She would = She’d |
|
It |
It would = It’d |
|
We |
We would = We’d |
|
They |
They would = They’d |
|
That |
That would = That’d |
|
These |
These would = These’d |
|
There |
There would = There’d |
|
Who |
Who would = Who’d |
|
What |
What would = What’d |
|
Where |
Where would = Where’d |
|
When |
When would = When’d |
|
Why |
Why would = Why’d |
|
How |
How would = How’d |
Had contractions list
|
had |
|
|
I |
I had = I’d |
|
You |
You had = You’d |
|
He |
He had = He’d |
|
She |
She had = She’d |
|
It |
It had = It’d |
|
We |
We had = We’d |
|
They |
They had = They’d |
|
That |
That had = That’d |
|
These |
These had = These’d |
|
There |
There had = There’d |
|
Who |
Who had = Who’d |
|
What |
What had = What’d |
|
Where |
Where had = Where’d |
|
Why |
Why had = Why’d |
|
How |
How had = How’d |
Have / Has contractions list
|
Have\has |
|
|
I |
I have = I’ve |
|
You |
You have = You’ve |
|
He |
He has = He’s |
|
She |
She has = She’s |
|
It |
It has = It’s |
|
We |
We have = We’ve |
|
They |
They have = They’ve |
|
That |
That has = That’s |
|
These |
These have = These’ve |
|
There |
There has = There’s |
|
Who |
Who has = Who’s |
|
What |
What have = What’ve |
|
Where |
Where has = Where’s |
|
Why |
Why has = Why’s |
|
How |
How have = How’ve |
Not contractions list
|
Not |
|
|
Is |
Is not = Isn’t |
|
Are |
Are not = Aren’t |
|
Was |
Was not = Wasn’t |
|
Were |
Were no = Weren’t |
|
Must |
Must not = Mustn’t |
|
Will |
Will not = Won’t |
|
Would |
Would not = Wouldn’t |
|
Dose |
Dose not = Doesn’t |
|
Do |
Do not = Don’t |
|
Did |
Did not = Didn’t |
|
Can |
Can not = Can’t |
|
Could |
Could not = Couldn’t |
|
Shall |
Shall not = Shan’t |
FAQs:
Here are 12 common contractions:
1. I’m (I am)
2. You’re (You are)
3. He’s (He is)
4. She’s (She is)
5. It’s (It is)
6. We’re (We are)
7. They’re (They are)
8. Can’t (Cannot)
9. Won’t (Will not)
10. Don’t (Do not)
11. Haven’t (Have not)
12. Isn’t (Is not)
The 6 most common contractions are:
1. I’m (I am)
2. You’re (You are)
3. He’s (He is)
4. It’s (It is)
5. Can’t (Cannot)
6. Don’t (Do not)
These are used frequently in everyday conversation.
Contracting words are shortened forms of two words combined with an apostrophe. For example:
1. I’m = I am
2. You’re = You are
3. He’s = He is
4. Can’t = Cannot
5. Won’t = Will not
6. Don’t = Do not
These are common in casual speech and writing.
Here are 6 examples of sentences with contractions:
1. I’m studying for the test.
2. You’re always so helpful.
3. He’s working on his project.
4. They’ve already left the party.
5. We can’t wait for the weekend.
6. It’s a beautiful day outside.
These contractions make the sentences sound more casual and conversational.
Contractions PDF
You May Also Like