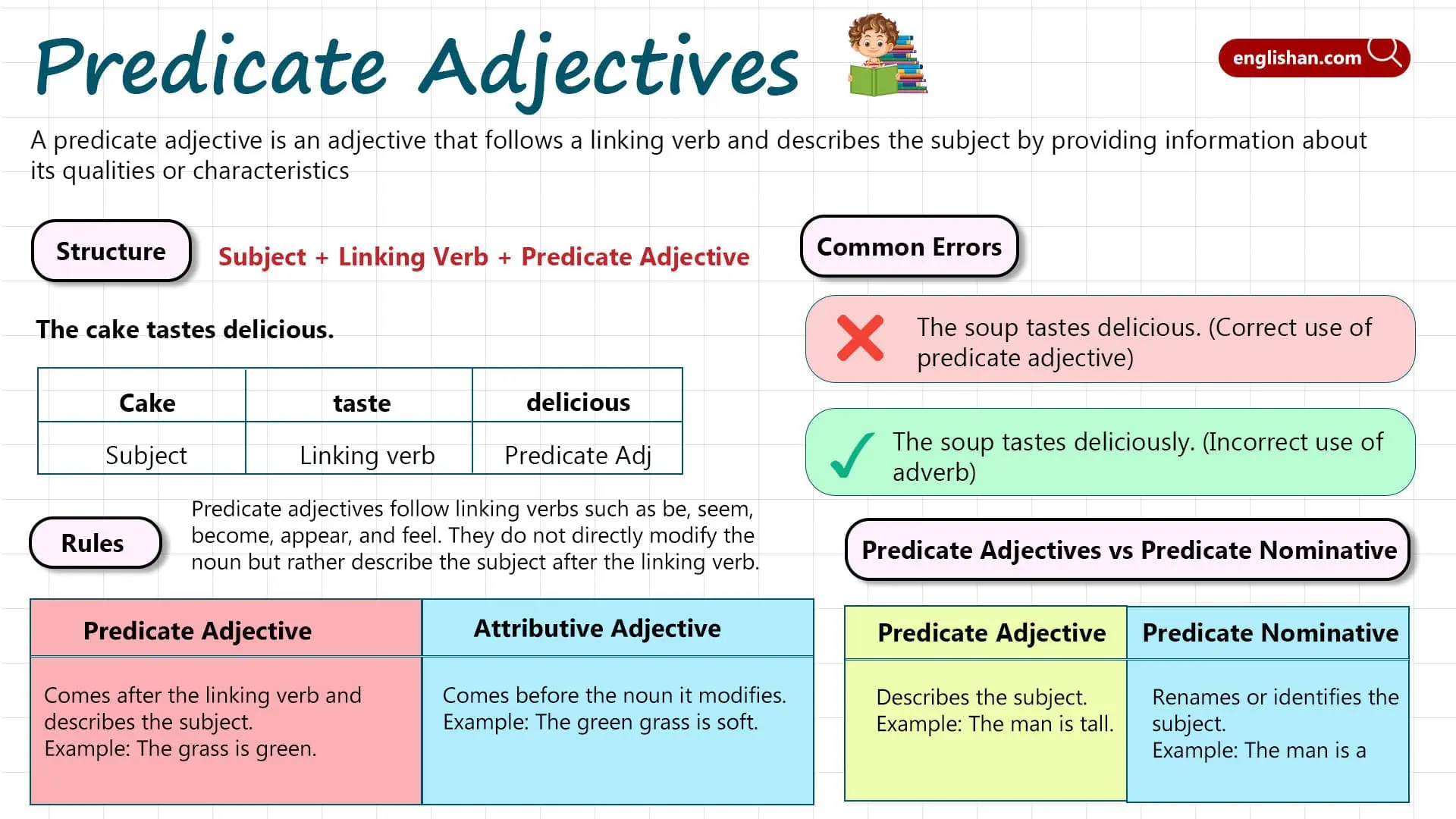
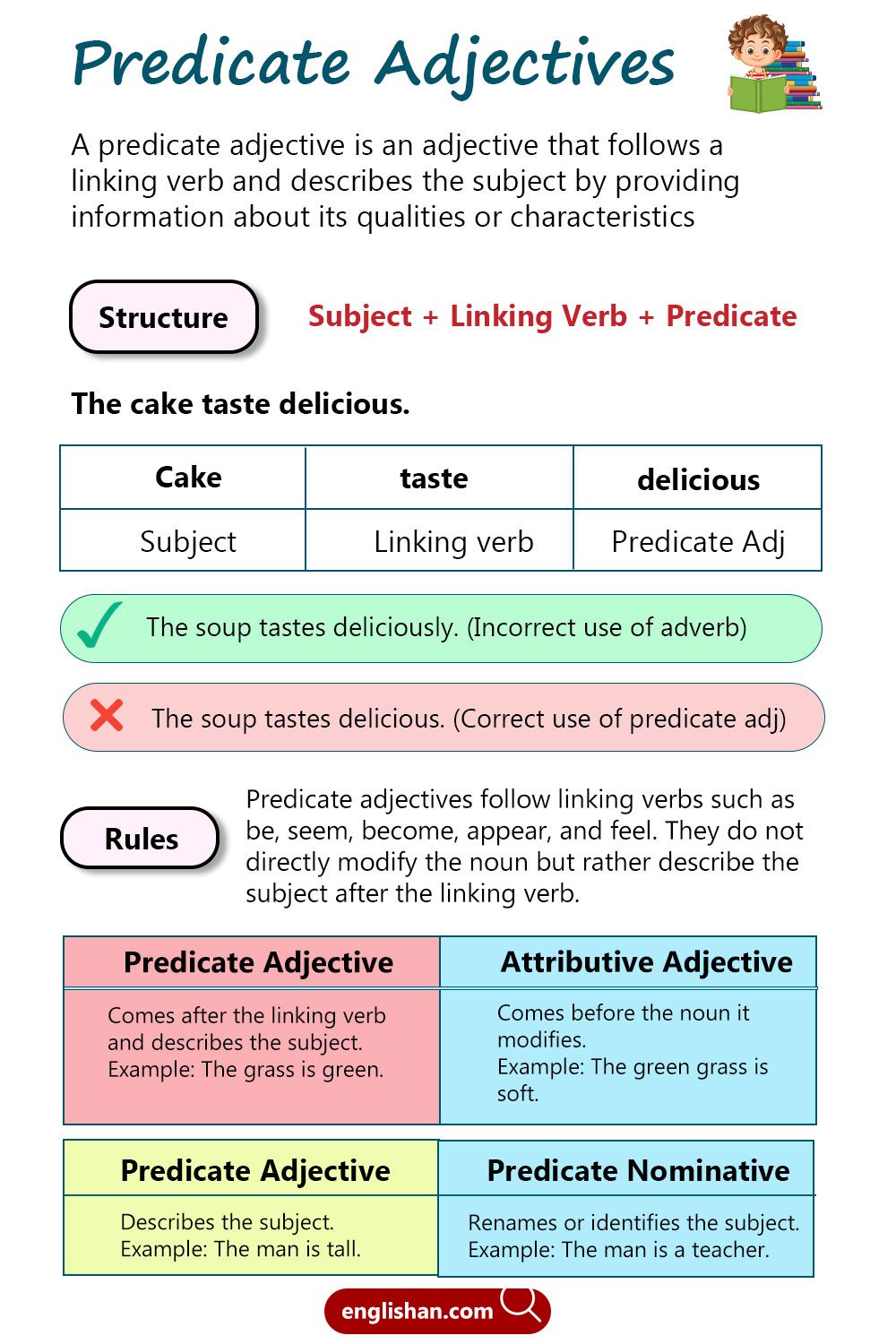
A predicate adjective is an adjective that follows a linking verb (such as is, seem, appear, become, etc.) and describes the subject of the sentence. It provides information about the subject’s qualities or characteristics.
Structure of Predicate Adjectives
The typical structure involving a predicate adjective looks like this: Subject + Linking Verb + Predicate Adjective
For example:
- The cake tastes delicious.
- He is tall.
In these examples, delicious and tall are adjectives describing the subjects cake and he, respectively.
Understanding Linking Verbs
To fully grasp predicate adjectives, it’s important to understand linking verbs. A linking verb connects the subject of the sentence to the adjective, but it does not express action. Instead, it serves as a bridge between the subject and its description.
Some common linking verbs include:
- Be (is, am, are, was, were)
- Seem
- Become
- Appear
- Feel
- Taste
- Look
For example:
- The flowers are beautiful. Here, are is the linking verb, and beautiful is the adjective that describes flowers.
How to Identify Predicate Adjectives?
To identify a predicate adjective in a sentence, follow these simple steps:
- Find the subject – Identify who or what the sentence is about.
- Locate the linking verb – Check if there is a linking verb connecting the subject to the rest of the sentence.
- Spot the adjective – Look for the word following the linking verb that is describing the subject.
Examples:
- The weather seems cold today.
- Subject: The weather
- Linking verb: seems
- Adjective: cold
- She looks happy.
- Subject: She
- Linking verb: looks
- Adjective: happy
Difference Between Predicate Adjectives and Attributive Adjectives
It’s important not to confuse predicate adjectives with attributive adjectives. Attributive adjectives directly modify the noun they describe and are placed before it, while predicate adjectives come after a linking verb.
Here’s a comparison:
Attributive Adjective:
- The green grass is soft.
Predicate Adjective:
- The grass is green.
Notice how the adjective green comes before the noun grass in the first sentence, but after the linking verb is in the second. This is a simple way to tell them apart.
Common Errors
Learners often make mistakes by using adjectives as though they were attributive adjectives or by using action verbs instead of linking verbs.
Incorrect Use:
- ❌ The soup tastes deliciously.
Here, deliciously is an adverb, but the word that follows the linking verb tastes should be an adjective.
Correct Use:
- ✅ The soup tastes delicious.
This is the correct way to use an adjective, as delicious is describing the soup’s taste.
Example Sentences
Let’s look at more examples to reinforce your understanding:
- The sky is blue.
- The flowers smell fresh.
- The movie was exciting.
- They seemed surprised by the news.
- The water feels cold.
In each of these examples, the adjectives (blue, fresh, exciting, surprised, cold) describe the subject and follow a linking verb.
Predicate Adjectives Vs Predicate Nominative
Though both are part of the predicate, it’s important to distinguish between a predicate adjective and a predicate nominative.
- A predicate adjective describes the subject.
- A predicate nominative renames or identifies the subject.
For example:
- The man is a teacher. (Predicate nominative: teacher)
- The man is tall. (Predicate adjective: tall)
Read More