Throughout this section of the course, you’ll gain comprehensive insights into the English present tense. The present tense in English comprises the following:
In this article, we’re going to learn about all the types of present tense. You’ll get a clear idea of when and how to use each one. There are also exercises to help you practice and understand these tenses better.
What Are Tenses?
Tenses in grammar indicate the time of an action. There are three main types: past, present, and future.
| Present | Past | Future | |
| Simple | I watch TV every evening. | I watched TV yesterday. | I will watch TV tomorrow. |
| Continuous | I am watching TV right now. | I was watching TV when the phone rang. | I will be watching TV at 8 PM tomorrow. |
| Perfect | I have watched TV already today. | I had watched TV before bedtime. | I will have watched TV by 9 PM. |
| Perfect Continuous | I have been watching TV for an hour. | I had been watching TV for two hours when you called. | By 10 PM tomorrow, I will have been watching TV for three hours. |
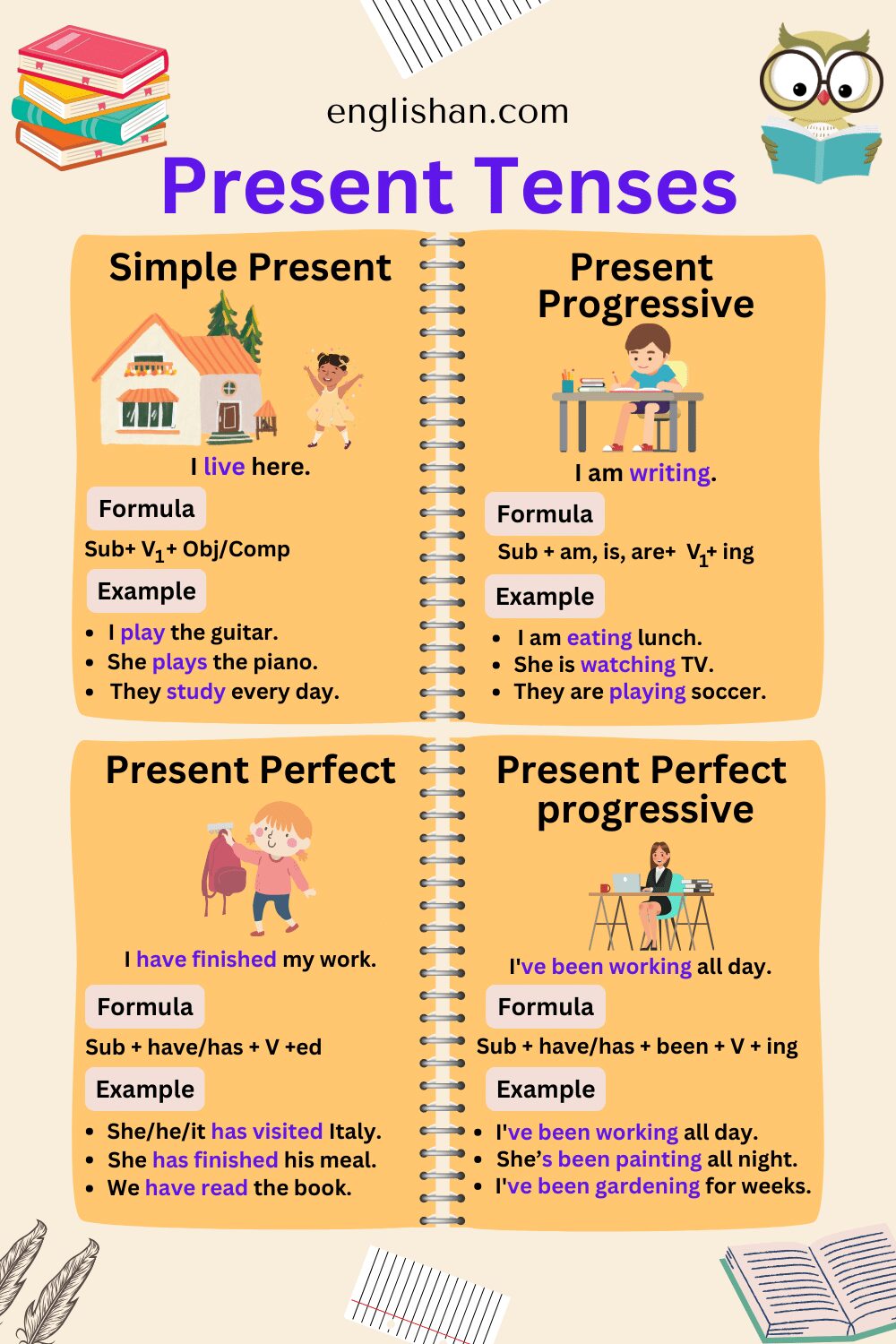
Simple Present Tense
The present tense is a verb tense used to express an action or a state of being that is occurring in the present. It is often used to describe habits, routines, general truths, or states that are consistently true. In English, the present tense is typically formed by using the base form of the verb, with no additional inflections or auxiliary verbs for the singular subjects (I, you, he, she, it) and the plural subjects (we, you, they).
Formation of Present Tense
- Subject + verb(1st form) + object.
- Subject + do not/does not + verb(1st form) + object.
- Do/Does + subject + verb (1st form) + object?
In any of the tenses, you can form positive, negative, or interrogative (a question) sentences.
| Person | Positive | Negative | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | I play soccer. | I do not play soccer. | Do I play soccer? |
| You | You play soccer. | You do not play soccer. | Do you play soccer? |
| We | We play soccer. | We do not play soccer. | Do we play soccer? |
| They | They play soccer. | They do not play soccer. | Do they play soccer? |
| He | He plays soccer. | He does not play soccer. | Does he play soccer? |
| She | She plays soccer. | She does not play soccer. | Does she play soccer? |
| It | It plays soccer. | It does not play soccer. | Does it play soccer? |
This table uses the sentence “I play soccer” as a base for illustrating positive, negative, and question sentences in the Present tense.
Uses of Present Tense
Let’s explore the uses of the present tense for the given scenarios:
Habits (Present)
- Example: I eat breakfast every morning. (The action of eating breakfast is a habitual activity.)
General Truths (Present)
- Example: The sun rises in the east. (A statement that is universally true and doesn’t change, expressed in the present tense.)
Repeated Actions or Events (Present)
- Example: She always arrives early for meetings. (The action of arriving early is a repeated behavior.)
Fixed Arrangements/Timetables (Present)
- Example: The train departs at 3 PM every day. (A scheduled departure time, expressed in the present tense.)
Feelings/Opinions/Beliefs (Present)
Examples:
- I believe in honesty. (Expressing a belief that is a constant aspect of one’s worldview.)
- He likes chocolate. (Expressing a preference or feeling that remains true over time.)
Instructions (Present)
- Example: Mix the ingredients thoroughly before baking. (Providing an instruction in the present tense.)
To get the Simple Present Tense, we need to know what “third person” means first.
Third person singular
In the third person singular (he/she/it), the addition of an “-s” to the verb is a standard practice, but there are a few rules to follow:
- For most verbs, simply append ‘-s’ to the base form:
- Runs
- Jumps
- Listens
- Drinks
- Writes
- If the verb ends in a ‘-y,’ replace the ‘y’ with ‘i’ before adding ‘-es’:
- Studies
- Flies
- Carries
- Buys
- Replies
- Verbs ending in specific letters (o, s, z, x, ch, and sh) require the addition of ‘-es’ at the end:
- Goes
- Fixes
- Buzzes
- Mixes
- Washes
- Boxes
- Watches
- Washes
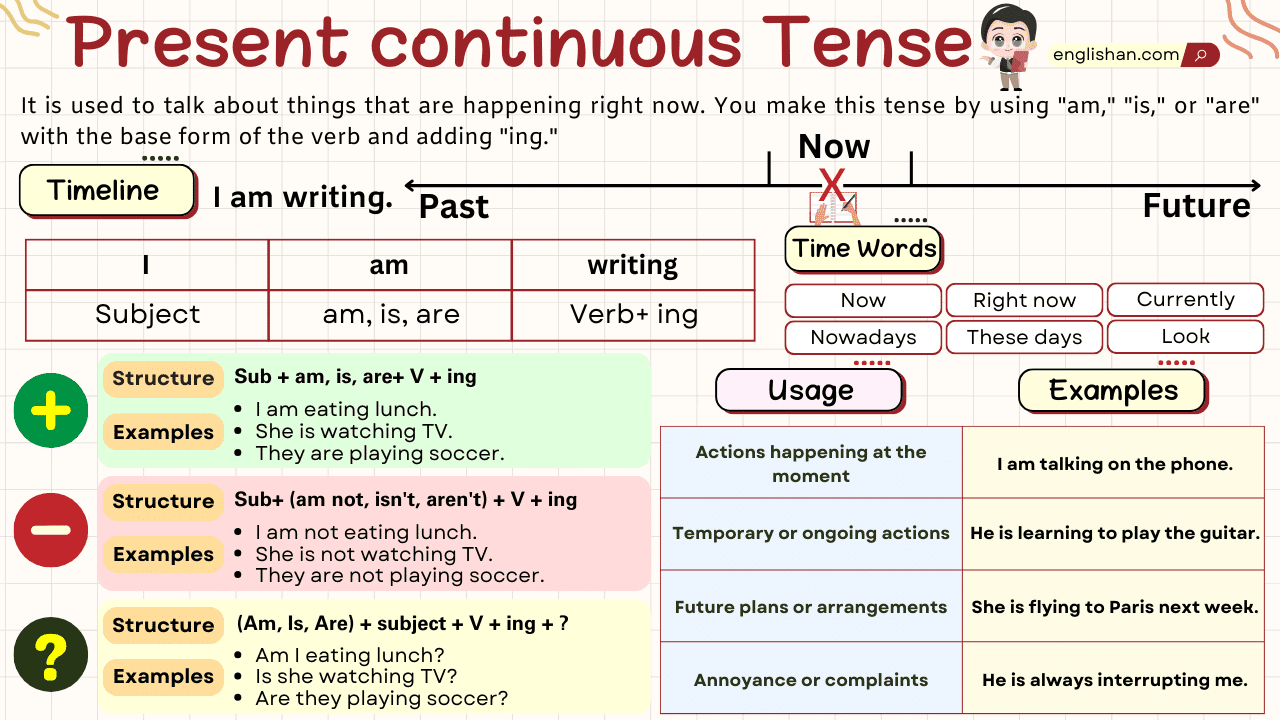
Present Continuous Tense
The present Continuous is sometimes called the present progressive; however, as most textbooks refer to it as the continuous, I will use that term here.
Formation of Present Continuous Tense
- Subject + is/am/are + verb(1st form) ing + object.
- Subject + is/am/are + not + verb(1st form) ing + object.
- Is/am/are + subject + verb (1st form) ing + object?
In any of the tenses, you can form positive, negative, or interrogative (a question) sentences.
| Person | Positive | Negative | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | I am eating. | I am not eating. | Am I eating? |
| You | You are eating. | You are not eating. | Are you eating? |
| We | We are eating. | We are not eating. | Are we eating? |
| They | They are eating. | They are not eating. | Are they eating? |
| He | He is eating. | He is not eating. | Is he eating? |
| She | She is eating. | She is not eating. | Is she eating? |
| It | It is eating. | It is not eating. | Is it eating? |
This table is based on the sentence “I am eating,” demonstrating the positive, negative, and question forms in the Present Continuous tense for various pronouns.
Uses of Present Continuous Tense with Examples
Let’s focus on the examples that involve the present continuous tense:
Actions happening in the moment (Present Continuous):
- Example: “I am reading a book.” (The action of reading is happening right now.)
Temporary events (Present Continuous):
- Example: “I am staying at a hotel for the week.” (The act of staying is temporary, and Present Continuous is used to emphasize the current duration.)
To complain or emphasize continuous behavior with words like ‘always’, ‘forever’, and ‘constantly’ (Present Continuous):
Examples:
- “She is constantly talking during the movie.” (Present Continuous, highlighting ongoing, irritating behavior.)
Present Perfect Tense
The next present tense is the present perfect. As highlighted in the main verb tense table above, it is constructed with have or has and the past participle form of the verb.
Formation of Present Perfect Tense
- Subject + has/have + verb(3rd form) + object.
- Subject +has/have + not + verb(3rd form) + object.
- Has/Have + subject + verb (3rd form) + object?
In any of the tenses, you can form positive, negative, or interrogative (a question) sentences.
| Person | Positive | Negative | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | I have completed the project. | I have not completed the project. | Have I completed the project? |
| You | You have completed the project. | You have not completed the project. | Have you completed the project? |
| We | We have completed the project. | We have not completed the project. | Have we completed the project? |
| They | They have completed the project. | They have not completed the project. | Have they completed the project? |
| He | He has completed the project. | He has not completed the project. | Has he completed the project? |
| She | She has completed the project. | She has not completed the project. | Has she completed the project? |
| It | It has completed the project. | It has not completed the project. | Has it completed the project? |
This table now uses the sentence “They have completed the project” as a base for illustrating positive, negative, and question forms in the present perfect tense.
Uses of Present Perfect Tense with Examples
Let’s elaborate on each of the uses of the present perfect with examples:
Actions that start in the past and continue to the present:
- Example: “She has worked at the company for 10 years.” (She started working in the past, and she continues to work there now.)
Life experiences, at an unspecified time in the past:
- Example: “I have visited Italy.” (The experience of visiting Italy occurred at some point in the past, but the exact time is not specified.)
Repeated action in an unspecified period:
- Example: “They have eaten sushi before.” (The action of eating sushi has happened at various times in the past, but the specific instances are not mentioned.)
Unfinished time (today, this week, this month, this year):
- Example: “I haven’t seen her today.” (The day is not finished, and there is still a possibility of seeing her later.)
A finished action with a present result:
- Example: “I have lost my keys.” (The action of losing the keys is complete, but the result, not having the keys, is present.)
Recent past with the words ‘just’, ‘recently’, ‘already’, and ‘yet’:
Examples:
- I have just finished my meal. (The meal was finished very recently.)
- They have recently moved to a new city. (They moved not long ago.)
- Have you already seen that movie? (Asking if you saw the movie recently.)
- He hasn’t finished his assignment yet. (The assignment is still not done.)
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
As implied by its name, this tense incorporates features from both the perfect and continuous tenses. Specifically, it combines have or has with the past participle been, followed by the verb+ing.
Formation of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Subject + (has/have)been + verb(1st form) ing + object + since/for.
- Subject +has/have + not + been + verb(1st form) ing + object + since/for.
- Has/Have + subject + been + verb (1st form) ing + object + since/for?
In any of the tenses, you can form positive, negative, or interrogative (a question) sentences.
| Person | Positive | Negative | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | I have been working since morning. | I have not been working since yesterday. | Have I been working since last week? |
| You | You have been exercising for an hour. | You have not been exercising for days. | Have you been exercising since yesterday? |
| We | We have been learning since the semester started. | We have not been learning for a long time. | Have we been learning for weeks? |
| They | They have been practicing for the competition. | They have not been practicing since the event began. | Have they been practicing since the last meeting? |
| He/She/It | He has been reading since he woke up. | He has not been reading for a while. | Has he been reading for hours? |
| It | It has been growing for months. | It has not been growing since it was planted. | Has it been growing since last summer? |
Uses of Present Perfect Continuous Tense with Examples
Let’s explore the uses of the present perfect continuous tense for the given scenarios:
Actions that started in the past and continue in the present:
Example:
- She has been living in this city for five years. (The action of living in the city started in the past and is still ongoing in the present.)
To emphasize the duration or ‘how long’ (with for and since):
Examples:
- They have been studying for three hours. (Emphasizing the ongoing duration of studying.)
- He has been working here since 2010. (Highlighting the continuous nature of his employment from a specific point in the past until now.)
Recently finished actions with present results:
Example:
- I have been painting the room, and it looks great now. (The action of painting was recently completed, and the present result is the great appearance of the room.)
Quiz:
-
- She usually ________ (go/goes) to the gym after work.
- They never ________ (eat/eats) meat.
- The sun ________ (rise/rises) in the east.
- We ________ (play/plays) tennis every weekend.
- He often ________ (read/reads) books in the evening.
- It usually ________ (rain/rains) a lot in the summer.
- I ________ (work/works) at a bank.
- The train ________ (leave/leaves) at 8 AM.
- She ________ (have/has) a dog named Max.
- We usually ________ (watch/watches) movies on Fridays.
- The teacher ________ (teach/teaches) English.
- The car ________ (not start/doesn’t start) in the cold weather.
- My parents ________ (live/lives) in the countryside.
- He ________ (drive/drives) a red car.
- The school bus ________ (arrive/arrives) at 7:30 AM.
- The children ________ (play/plays) in the park every afternoon.
- I ________ (speak/speaks) three languages.
- The alarm clock ________ (ring/rings) at 6 AM.
Answers:
- goes
- eat
- rises
- play
- reads
- rains
- work
- leaves
- has
- watch
- teaches
- doesn’t start
- live
- drives
- arrives
- play
- speak
- rings
FAQs
The main present tenses are present, present continuous, present perfect, and present perfect continuous.
The present tense is used for general facts, habits, routines, and timeless situations.
It is formed using the present tense of the verb “to be” (am/are/is) + the present participle (verb + -ing).
The present continuous is used for actions happening now, temporary actions, and future arrangements.
It is formed using the present tense of the auxiliary verb “have” (have/has) + the past participle of the main verb.
It is formed using the present perfect of the auxiliary verb “have” (have/has) + been + the present participle (verb + -ing).
You May Also Like
Get Printable Worksheets on English Tenses and Check Your Understanding