Understanding weak verbs is one of the easiest ways to improve your English grammar. These verbs, which form their past tenses by simply adding -ed, -d, or -t, are more common than you might think. Yet, many learners struggle with them, often confusing them with stronger verb forms or irregular ones.
But once you get the hang of weak verbs, you’ll see how they help you express past actions clearly and consistently. In this article, we’ll break down the types of weak verbs, their usage and examples so you can start using them confidently in your own writing and speaking.
What is a Weak Verb?
A weak verb is a verb that makes its past tense and past participle by adding a regular ending, usually:
- “-ed” (e.g., walk → walked)
- “-d” (e.g., love → loved)
- “-t” (e.g., burn → burnt in British English)
What makes weak verbs stand out is that they follow a predictable pattern, unlike strong verbs, which change their vowel sounds to form the past tense (for example, “sing” becomes “sang”). This consistency makes weak verbs easier to use and more accessible for learners of all levels.
While all regular verbs are weak verbs, not all weak verbs are regular. Some weak verbs follow slightly irregular patterns, but they still maintain that same easy-to-understand structure of adding an ending to form the past tense.
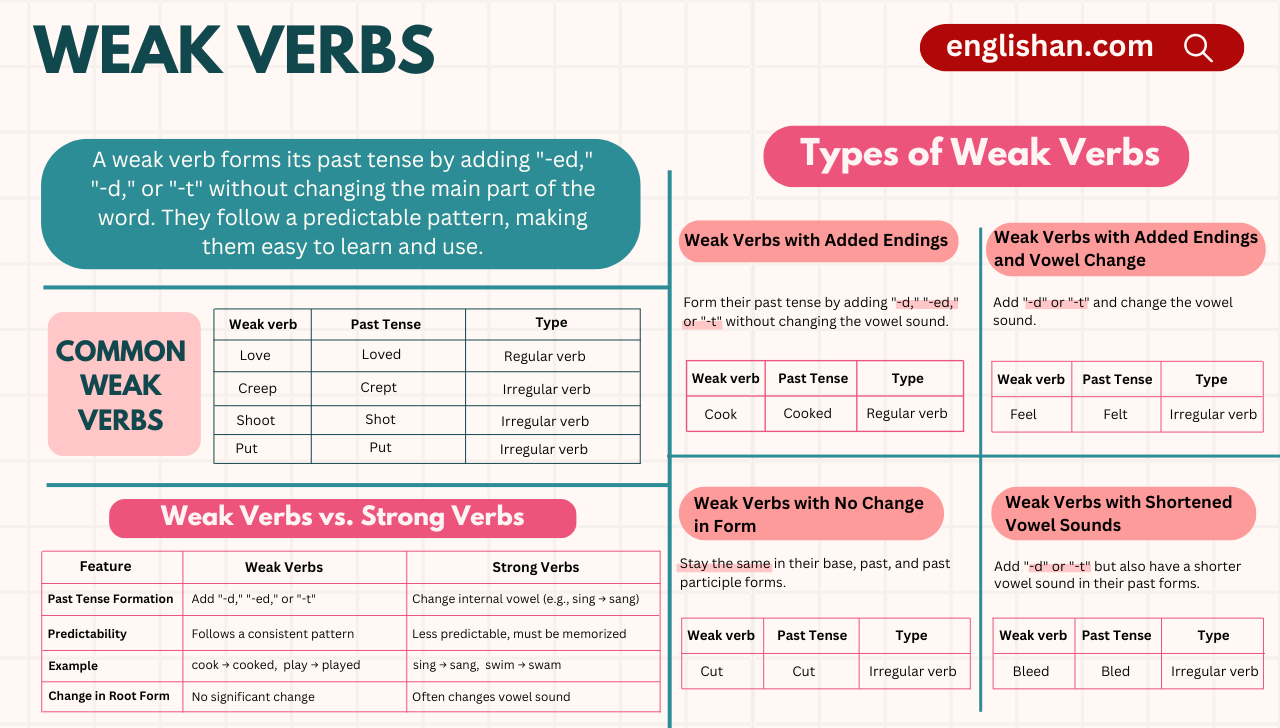
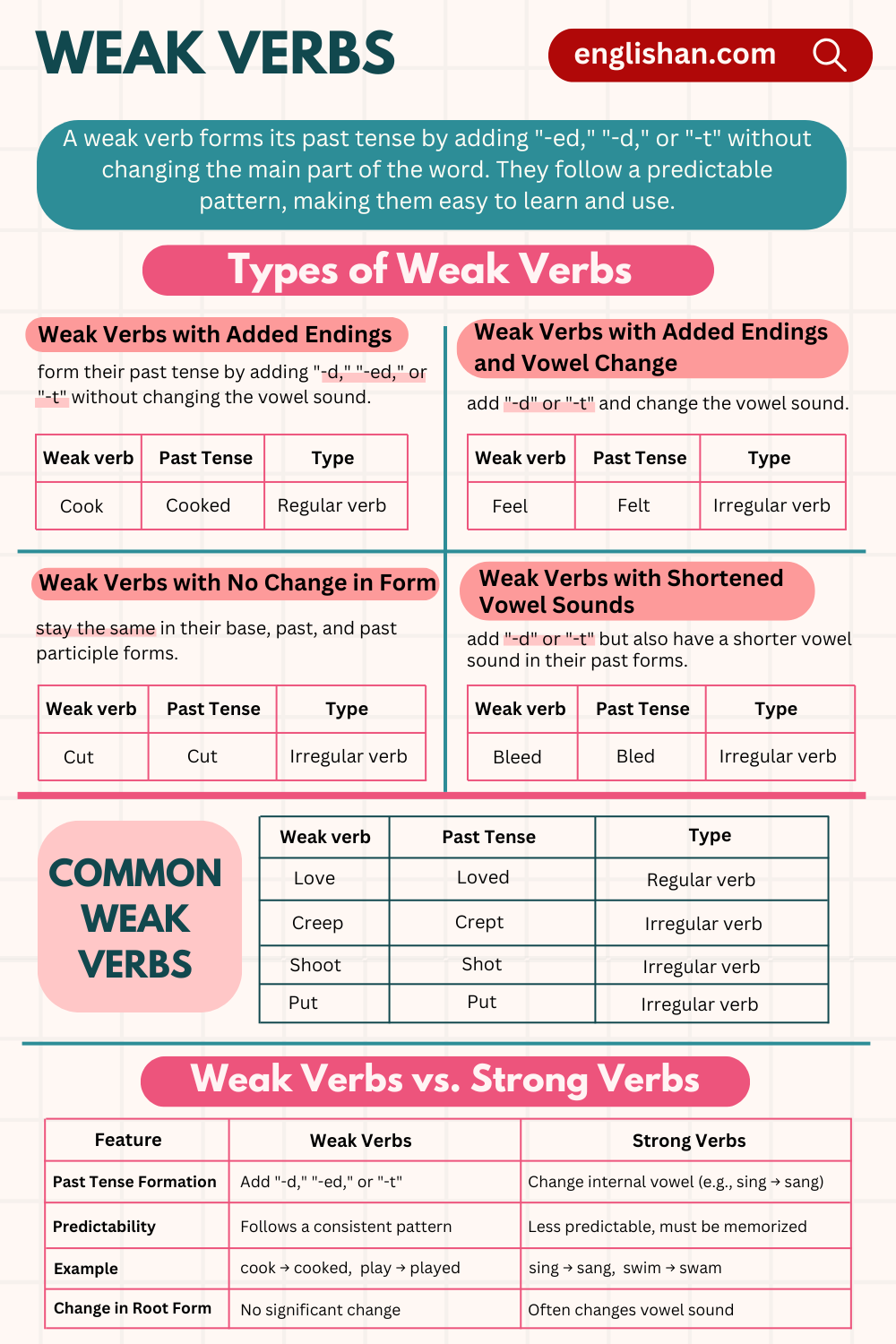
4 Basic Types of Weak Verbs
There are different types of weak verbs in English, and each has its own unique way of forming the past tense. Understanding these types can help you use weak verbs correctly in any context. Let’s take a closer look at each type:
1. Weak Verbs with Regular Endings (“-ed,” “-d,” or “-t”)
The most straightforward weak verbs are those that form their past tense by adding -ed, -d, or -t. These are what we typically call regular verbs.
| Weak Verb | Simple Past Tense | Past Participle | Comment |
| cook | cooked | has cooked | regular verb |
| walk | walked | has walked | regular verb |
| start | started | has started | regular verb |
These verbs are easy to spot because they always follow the same rule: just add -ed or -d to the base verb. So, “talk” becomes “talked,” and “love” becomes “loved.” Simple!
2. Weak Verbs with Vowel Changes
While some weak verbs follow the regular -ed or -d pattern, others add -d or -t while also changing the vowel sound in the past tense. These verbs are often considered irregular, but they still form the past tense with a regular ending, making them a type of weak verb.
| Weak Verb | Simple Past Tense | Past Participle | Comment |
| feel | felt | has felt | irregular verb |
| keep | kept | has kept | irregular verb |
| build | built | has built | irregular verb |
Even though these verbs change the vowel in their past tense form, they still follow a pattern of adding an ending, so they remain weak verbs.
3. Weak Verbs with Shortened Vowel Sounds
In some cases, the vowel sound changes slightly in the past tense, but the -ed or -t ending still applies. This makes the past tense form sound a little different from the base verb, but the structure remains regular.
| Weak Verb | Simple Past Tense | Past Participle | Comment |
| bleed | bled | has bled | irregular verb |
| lead | led | has led | irregular verb |
| read | read | has read | irregular verb |
These verbs are a bit trickier since the vowel sounds shorten in the past tense, but the rule of adding -ed or -t remains.
4. Weak Verbs with No Change in Form
Some weak verbs don’t change at all in their past tense or past participle form. While these verbs seem irregular, they actually follow a regular pattern, which is why they are still considered weak verbs.
| Weak Verb | Simple Past Tense | Past Participle | Comment |
| cut | cut | has cut | irregular verb |
| set | set | has set | irregular verb |
| hit | hit | has hit | irregular verb |
Though they don’t change form, these verbs are considered irregular because of their lack of transformation between the base, past tense, and past participle forms.
Most Frequently Used Examples of Weak Verb in English
Here are some examples of weak verbs that you’ll often encounter in both spoken and written English. These verbs are important to understand, as they will help you talk about past actions in a more consistent way.
| Weak Verb | Simple Past Tense | Past Participle | Type |
| love | loved | has loved | regular verb |
| play | played | has played | regular verb |
| creep | crept | has crept | irregular verb |
| shoot | shot | has shot | irregular verb |
| put | put | has put | irregular verb |
Notice how some of these verbs, like “love” and “play,” are regular, while others, like “creep” and “shoot,” follow an irregular pattern but still fit the definition of weak verbs.
Regular Verbs vs. Weak Verbs
The terms weak verbs and regular verbs are often used interchangeably, but they’re not exactly the same. All regular verbs are weak verbs, but not all weak verbs are regular. Let’s break it down:
- Regular verbs always follow the same rule for creating the past tense: they add -ed or -d. For example, “talk” becomes “talked,” and “love” becomes “loved.”
- Weak verbs, however, are a broader category. They include regular verbs, but also some irregular verbs that follow a similar pattern, even if their vowel sounds change. For example, “feel” becomes “felt,” and “keep” becomes “kept.”
So while all regular verbs are weak verbs, not all weak verbs are regular. The term “weak verb” encompasses both regular and certain irregular verbs. Similarly, the terms “irregular verb” and “strong verb” are also not the same:
- Strong verbs change their vowel sounds when they form the past tense (like “sing” to “sang”).
- Irregular verbs can be either weak or strong, depending on whether they follow regular endings or not.
Why Do Weak Verbs Matter in English?
Weak verbs are crucial for mastering English grammar because they simplify the process of forming past tenses. When you understand how to use weak verbs, you’ll be able to express past actions clearly and with confidence. Whether you’re writing a story, giving a speech, or simply having a conversation, weak verbs will help you communicate more effectively.
Conclusion
To sum up, we can say that understanding weak verbs is all about recognizing their simple and consistent patterns. Whether you’re learning to form past tenses with regular verbs like “talked” or tackling slightly more complex forms like “felt” or “kept,” weak verbs make English a lot easier to understand.
The more you practice these verbs, the more naturally they’ll come to you, helping you sound more fluent and accurate when speaking and writing. So, next time you need to talk about something that happened in the past, remember, weak verbs have got you covered.
Ready to Master English Grammar?
Now that you have a clear understanding of weak verbs, why not take your grammar skills to the next level? Check out our other articles on English composition to learn more essential tips, tricks, and exercises to improve your writing and fluency. Don’t miss out on mastering key concepts like sentence structure, verb tenses, and more!
You May Also Like