A noun phrase is a combination of a noun and its modifiers, like adjectives or determiners, that gives more detail about the noun. It plays a significant role in sentence structure, helping to give more specific information or context. These phrases are very common in English and are used in both simple and complex sentences. Mastering noun phrases allows you to express ideas more clearly and make your sentences richer in detail.
Here are some examples of noun phrases:
| Type of Noun Phrase | Example |
| Simple | book |
| With a modifier | the beautiful flower |
| With multiple modifiers | a tall, handsome man |
| With a determiner | these toys |
| With a prepositional phrase | the house with a red door |
| With an adjective clause | the student who won the award |
In each example, the core element is the noun (book, man, flower, door, student), and additional words provide more information about or modify that noun. Noun phrases are essential components of sentences and play a crucial role in conveying meaning and context.
Noun Phrase Structure
A noun phrase (NP) is a phrase based around a noun, which serves as the head of the phrase. It typically consists of the noun and its modifiers. The structure of a noun phrase can vary, but it generally includes the following components:
Head Noun
The core element of the noun phrase is the head noun, which is the main noun that the phrase is centered around. This noun gives the essential meaning to the phrase.
- Example: dog, book, teacher
Determiners
These are words that introduce and modify the noun. Determiners can be definite articles (the), indefinite articles (a, an), demonstratives (this, that, these, those), possessives (my, your, his, her, its, our, their), quantifiers (some, many, few), or numbers.
- Example: a dog, the book, my teacher
Adjectives
Adjectives modify the noun, providing additional information about its qualities or characteristics.
- Example: big dog, interesting book, knowledgeable teacher
Prepositional Phrases
These are phrases that begin with a preposition (such as in, on, under, with) and provide additional information about the noun.
- Example: dog with a big tail, book on the shelf, a teacher in the classroom
Modifiers
Other modifiers, such as relative clauses or participial phrases, can also be part of a noun phrase. These provide more details or descriptions about the noun.
- Example: a dog that barks loudly, a book written by t famous author, a teacher teaching the advanced class
Here are a few examples illustrating the structure of noun phrases:
- A (determiner) big (adjective) black (adjective) cat (head noun).
- The (determiner) cat (head noun) on the roof (prepositional phrase).
- An (Determiner) interesting (Adjective) article (Noun) about artificial intelligence (Prepositional Phrase) caught my eye.
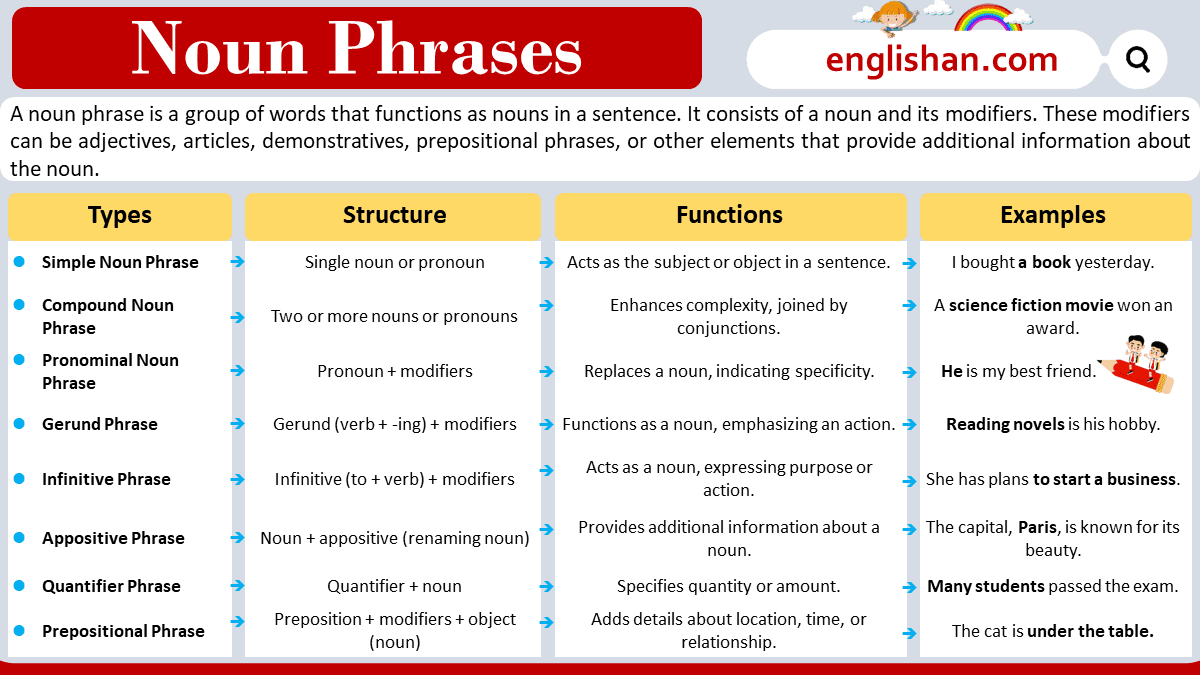
Types of Noun Phrases
Here are some basic types of noun phrases:
Simple Noun Phrase
- Structure: [Determiner] + [Noun]
A simple noun phrase consists of a single noun along with its determiners (articles, demonstratives, possessives) and modifiers (adjectives).
- Example: the cat, a book, my friend
Compound Noun Phrase
- Structure: [Determiner] + [Adjective(s)] + [Noun] + [Conjunction] + [Determiner] + [Adjective(s)] + [Noun]
A compound noun phrase involves two or more nouns joined together. Adjectives can modify each noun independently. These nouns can be connected by coordinating conjunctions or prepositions.
- Example: bread and butter, the king of England
Pronominal Noun Phrase
- Structure: [Pronoun] + [Prepositional Phrase]
Pronominal noun phrases replace a noun with a pronoun (he, she, it, etc.) and may include a prepositional phrase for additional information.
- Example: he, those people, your idea
Gerund Phrase
- Structure: [Gerund] + [Object] + [Prepositional Phrase]
Gerund phrases involve a gerund (a verb ending in -ing functioning as a noun) and can include an object and/or prepositional phrase.
- Example: swimming in the pool, reading a book
Infinitive Phrase
- Structure: [Infinitive] + [Object] + [Prepositional Phrase]
Infinitive phrases consist of an infinitive verb (to + base form of the verb) along with an object and/or prepositional phrase.
- Example: to eat lunch, to explore new places
Appositive Phrase
- Structure: [Noun] + [Appositive] + [Modifiers]
Appositive phrases provide additional information about a noun and are often set off by commas. They can include modifiers for further description.
- Example: My friend, the doctor, the city,
Quantifier Phrase
- Structure: [Quantifier] + [Determiner] + [Adjective(s)] + [Noun]
Quantifier phrases incorporate words that express quantity, such as many, few, several, etc., along with determiners and adjectives.
- Example: Many bright students, few opportunities
Prepositional Phrase
- Structure: [Preposition] + [Modifiers] + [Noun]
A prepositional phrase includes a preposition, its object (usually a noun), and any modifiers of the object.
- Example: in the morning, with a smile on her face
Functions of Noun Phrase
The primary functions of a noun phrase in a sentence include:
- Subject: They can function as the subject of a sentence, performing the action or being the topic.
- Object: Noun phrases can act as the direct or indirect object of a verb, receiving the action or indicating to whom or what the action is done.
- Complement: They can serve as a complement, providing additional information about the subject or object.
- Modifier: Noun phrases can function as modifiers, adding details to other nouns or pronouns in a sentence.
- Appositive: They can be used as appositives, offering further explanation or clarification about another noun or pronoun.
- Predicate Nominative: In sentences with linking verbs, a noun phrase can serve as a predicate nominative, renaming or restating the subject.
Examples
- The bright sun
- A blue sky
- The spicy food
- Many colorful flowers
- The tall building
- My best friend
- A cup of hot coffee
- A beautiful sunset
- The quiet room
- A new opportunity
- The early morning
- A pair of comfortable shoes
- An important meeting
- A stack of colorful notebooks
- My best friend from school
- An interesting book on history
- A delicious slice of pizza
- The busy streets of the city
- A bouquet of fresh flowers
- A box of chocolates on the table
FAQs
A noun phrase follows this pattern:
(Words before the noun) + Noun + (Words after the noun)
Here are examples of phrases, categorized into different types:
1. Noun Phrase
The big red balloon
My favorite book
2. Verb Phrase
Is running quickly
Has been working hard
3. Adjective Phrase
Extremely happy with the results
Full of excitement
4. Adverb Phrase
Very quietly in the room
Quickly without hesitation
5. Prepositional Phrase
On the table
Under the bright moonlight
6. Infinitive Phrase
To finish the project
To explore new places
A noun phrase functions as a subject, object, or complement in a sentence. It can also work as the object of a preposition.
Key Functions:
1. Subject: Performs the action.
The little boy ran fast.
2. Object: Receives the action.
She loves chocolate cake.
3. Complement: Renames or describes the subject.
My favorite dessert is apple pie.
4. Object of a Preposition: Completes a prepositional phrase.
He sat under the shady tree.
The number of noun phrases in a sentence depends on how many nouns or pronouns (with their modifiers) are present as subjects, objects, or complements.
Example:
The small boy played with a red ball.
Noun Phrases: The small boy, a red ball
You May Also Like
- Nouns Worksheets with Answers
- Adverbial Phrases with Examples
- Types of Phrases with Examples
- Types of Clauses with Examples
- Phrases and Clauses with Examples
- Predicate Adjectives in English