Relative clauses are essential parts of sentence structure that begin with a relative pronoun (such as who, whom, whose, which, or that) and function as an adjective in a sentence. They help us provide more information about the people, places, and things. They can make our writing more descriptive and clear by providing extra details that help the reader understand what we are talking about. In this article, we will define relative clauses, explain their types, discuss their usage, and provide examples to help you understand how to use them effectively. So, let’s get started!
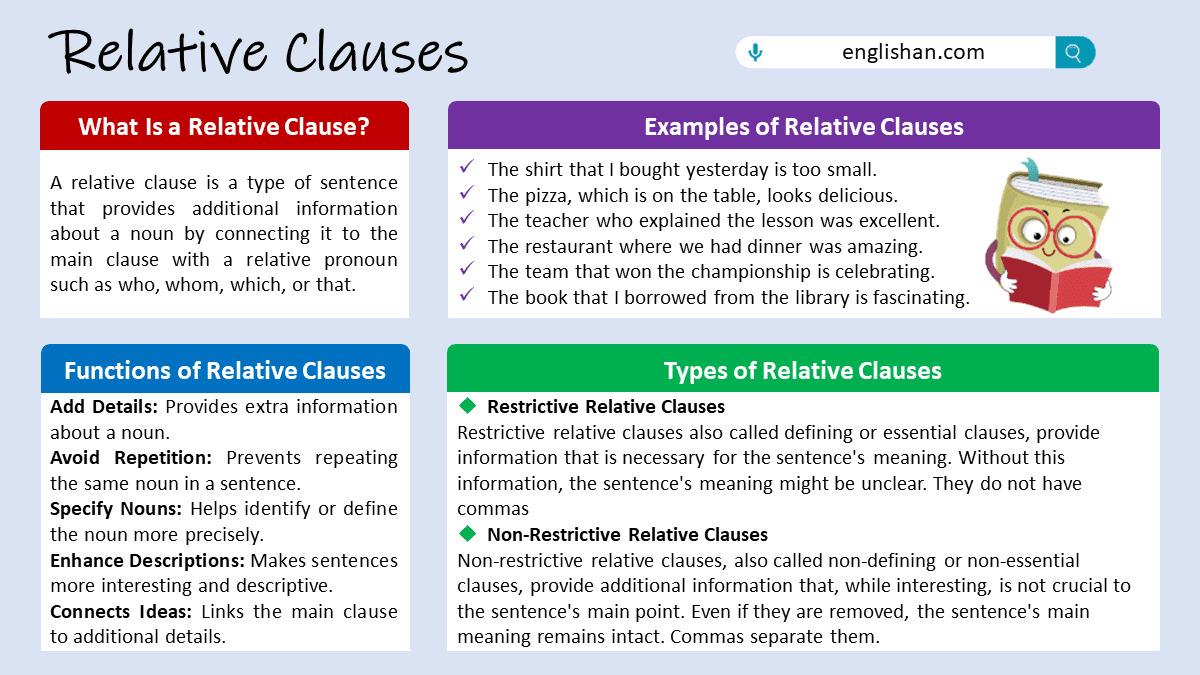
What is a Relative Clause?
A relative clause is a type of sentence that provides additional information about a noun by connecting it to a relative pronoun such as who, whom, which, or that. It functions as a subordinate clause within a larger sentence and helps to clarify the identity or nature of the noun it modifies. Relative clauses are made up of a relative pronoun, verb, and any necessary details. They are called relative because they relate a noun to another part of the sentence.
In simple words, They’re like mini-sentences that are connected to a main clause by a relative pronoun, such as “who,” “which,” “that,” or “whose,” and provide additional details about the noun it is modifying. For example, in the sentence “The woman who lives next door is a doctor,” the relative clause “who lives next door” provides more information about the noun “woman.” Relative clauses can be used to clarify the identity, location, or characteristics of a noun. They can also be used to add complexity and detail to a sentence. In addition, relative clauses can be used to replace entire sentences or phrases with shorter expressions.
Examples:
- The shirt that I bought yesterday is too small.
- The cake that my mom baked was delicious.
- The teacher who explained the lesson was excellent.
- The restaurant where we had dinner was amazing.
- The team that won the championship is celebrating.
Types of Relative Clauses
Relative clauses, also known as adjective clauses, provide additional information about a noun in a sentence. There are two basic types of relative clauses: restrictive (defining) and non-restrictive (non-defining).
Restrictive Relative Clauses
Restrictive relative clauses, also called defining or essential clauses, provide information that is necessary for the sentence’s meaning. Without this information, the sentence’s meaning might be unclear. Commas do not separate them.
Examples:
- The girl who lives next door is my friend.
- The car that is parked in the driveway is mine.
- The student who won the award is excited.
- The girl who is wearing a red dress is my sister.
- The book that I borrowed from the library is fascinating.
Characteristics:
- No commas are used to separate the restrictive relative clause from the rest of the sentence.
- The information in the clause is crucial for identifying the noun.
Non-Restrictive Relative Clauses
Non-restrictive relative clauses, also called non-defining or non-essential clauses, provide additional information that, while interesting, is not crucial to the sentence’s main point. Commas separate them.
Examples:
- My sister, who is wearing a red dress, just arrived.
- My friend, who is a great artist, painted this.
- The mountain, which is covered in snow, is breathtaking.
- My laptop, which I bought last year, is now outdated.
- The novel, which I borrowed from the library, is fascinating.
Characteristics:
- Commas are used to set off the non-restrictive relative clause from the rest of the sentence.
- The information in the clause adds extra detail but is not necessary for identification.
Functions of Relative Clauses
1. Identification:
- Function: Helps identify which person, thing, or place we are talking about.
- Example: The girl who lives next door is my friend.
2. Description:
- Function: They provide additional details to describe the noun in more depth.
- Example: The book that I borrowed from the library is fascinating.
3. Possession:
- Function: Relative clauses using “whose” indicate ownership or possession of the noun.
- Example: The man whose car broke down needs assistance.
4. Location:
- Function: Relative clauses with “where” describe a specific place related to the noun.
- Example: The park, where we had a picnic last summer, is beautiful.
5. Time:
- Function: They can convey information about when an action took place.
- Example: The day when we first met was unforgettable.
6. Reason:
- Function: Relative clauses explain the reason behind an action or situation.
- Example: The student who studied diligently aced the exam.
7. Clarification:
- Function: Clarifies the noun, reducing ambiguity in the sentence.
- Example: The city where I was born is very lively.
8. Additional Information:
- Function: Adds extra, non-essential details to make the sentence more interesting.
- Example: My friend, who is a great artist, painted this.
Relative Pronouns List
Relative pronouns are words that introduce relative clauses, providing more information about a noun in a sentence. They connect the main clause to the relative clause, serving as a bridge to give additional details. Here is a list of common relative pronouns used in relative clauses:
- That
- Who
- Why
- Whom
- Whose
- Which
- Where
- When
Relative Clauses Examples
- The book that I bought yesterday is fantastic.
- The girl, who is my neighbor, is friendly.
- The pizza, which is on the table, looks delicious.
- The car that belongs to my brother is blue.
- The house, where I grew up, is near the park.
- The shirt, which is in the closet, is new.
- The flowers that bloom in spring are colorful.
- The girl who won the race is my classmate.
- The boy who is wearing glasses is my cousin.
- The cake, which my mom baked, is delicious.
- The boy who won the award is my friend.
- The book that I’m reading is interesting.
- The phone, which is on the table, is ringing.
- The car that needs repairs is in the garage.
- The movie that you recommended was great.
Relative Clauses Exercises
1. Which sentence has a relative clause?
- The sun is shining brightly.
- The girl who won the race is my friend.
- I like ice cream.
- He reads a book every night.
2. What is the relative pronoun in the sentence: “The cat that is sleeping is mine.”?
- The
- Is
- That
- Sleeping
3. Which sentence has a non-restrictive relative clause?
- The dog that barks loudly belongs to my neighbor.
- My friend, whose birthday is today, is throwing a party.
- The car that needs repairs is in the garage.
- The flowers that bloom in spring are colorful.
4. Choose the correct relative pronoun: “I have a friend ______ sister is a doctor.”
- Whose
- Who
- Which
- Whom
5. Identify the restrictive relative clause: “The movie that made me cry is a drama.”
- A drama
- The movie
- That made me cry
- Is
6. What is the relative pronoun for a person that is the object of a verb?
- Whose
- That
- Whom
- Who
7. What is the correct relative pronoun for the subject of a verb?
- That
- Which
- Who
- Whose
8. Which relative pronoun indicates possession?
- Who
- Whom
- Whose
- Which
9. The girl __________ is standing by the door is my sister.
- Who
- Which
- Whose
- Whom
10. The restaurant __________ we had lunch is excellent.
- Which
- Where
- When
- Whose
Answers:
- The girl who won the race is my friend.
- That
- My friend, whose birthday is today, is throwing a party.
- Whose
- That made me cry
- Whom
- Who
- Whose
- Who
- Where
FAQs
A relative clause is a group of words that begins with a relative pronoun (such as who, whom, whose, which, or that) and functions as an adjective. It provides additional information about a noun in a sentence, specifying which person or thing we are talking about.
The primary purpose of a relative clause is to give more information about a noun, making the sentence more precise and descriptive. It helps clarify which person, thing, or place we are referring to and adds depth to the overall meaning of the sentence.
Common relative pronouns include who, whom, whose, which, and that. These words introduce relative clauses and connect them to the nouns they modify.
A restrictive clause is essential to the sentence’s meaning and doesn’t have commas. A non-restrictive clause provides extra information and is separated by commas.
Common relative pronouns include:
1. Who: Referring to people.
2. Whom: Referring to the object of a verb or preposition.
3. Whose: Indicating possession.
4. Which: Refers to things or animals.
5. That: Used for both people and things.
Read More
- Adverbial Clauses
- Dependent Clauses
- Independent Clauses
- Clauses And Their Types
- Clauses with Examples and Functions