Contents
Pronouns play a crucial role in English grammar by helping us avoid unnecessary repetition. Instead of using the same noun repeatedly, pronouns can replace them, making sentences clearer and easier to read. A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun or noun phrase. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into what pronouns are, how they function, and the different types of pronouns used in English.
What is a Pronoun?
A pronoun is a word that substitutes for a noun. For example, instead of saying “John went to John’s car,” we can say “John went to his car.” The word his is a pronoun that takes the place of “John’s.” This makes sentences more natural and less repetitive.
The Antecedent of a Pronoun
Before using a pronoun, it’s important to identify its antecedent. The antecedent is the noun or noun phrase that the pronoun refers to. For example:
- Sarah loves her cat.
In this sentence, Sarah is the antecedent of the pronoun her. The antecedent helps readers understand who or what the pronoun is referring to.
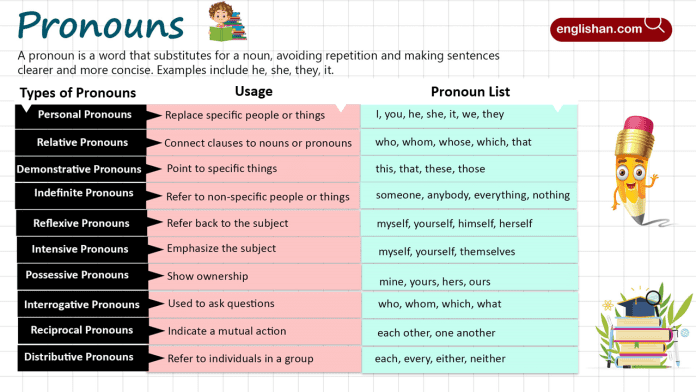
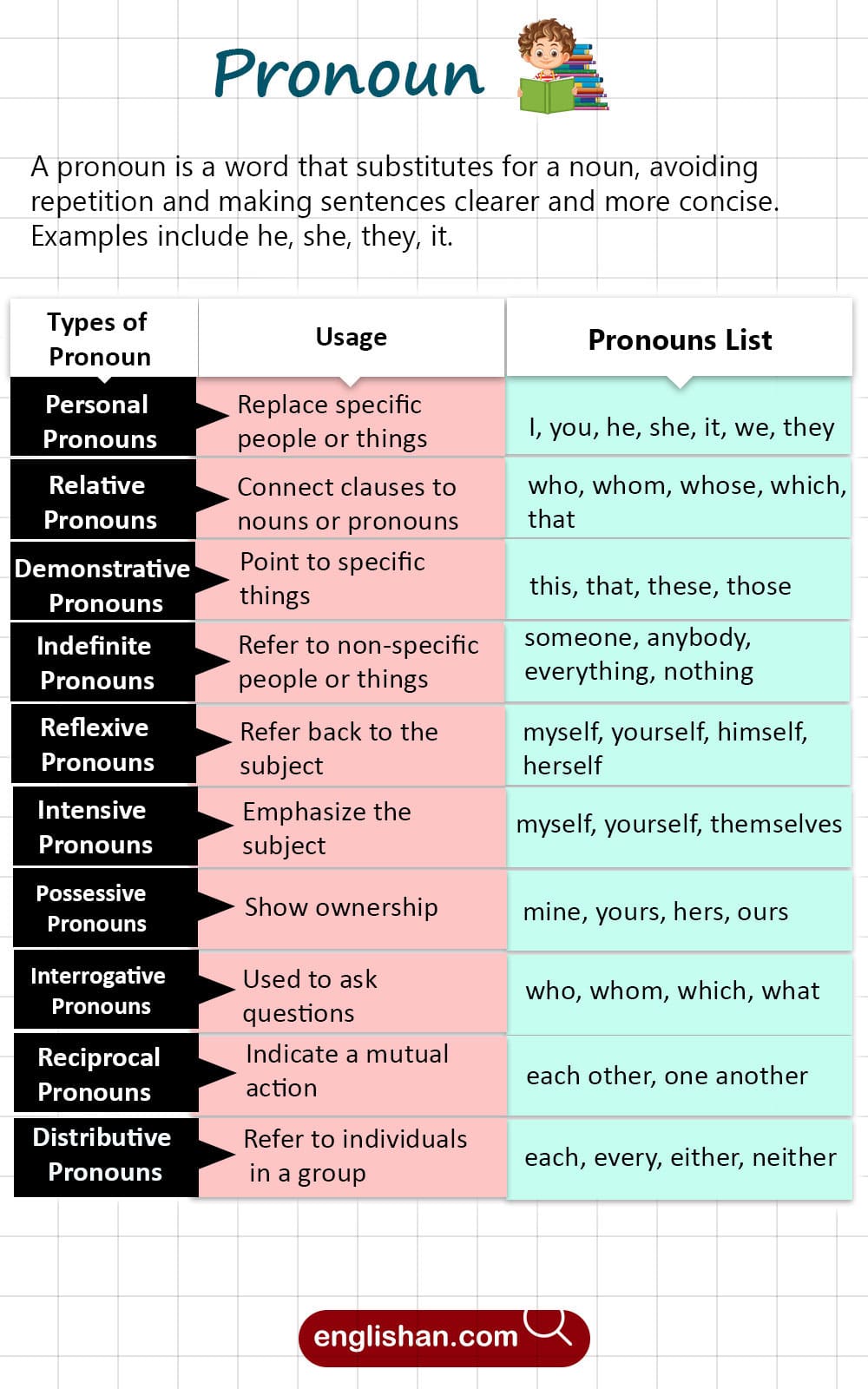
Types of Pronouns
There are several types of pronouns in English. Each type has a specific role and function in sentences. Let’s explore these types in detail.
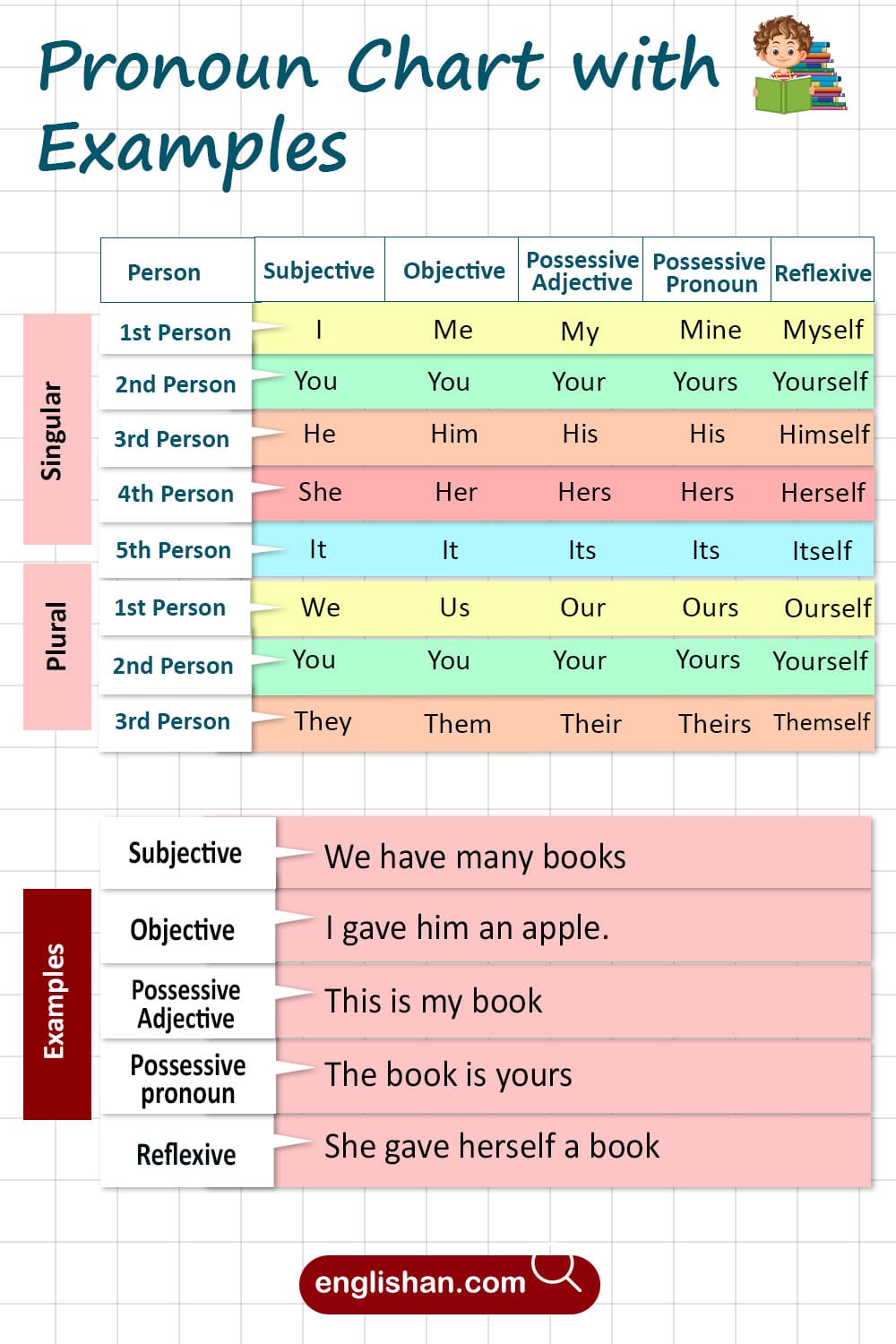
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns refer to specific people or things. They change form based on their role in the sentence (subject or object). Here’s a breakdown of personal pronouns:
| Subject Pronouns | Object Pronouns |
| I | Me |
| You | You |
| He/She/It | Him/Her/It |
| We | Us |
| They | Them |
Examples in sentences:
- He is going to the store.
- Can you help me with this?
Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses and refer back to a noun mentioned earlier. Common relative pronouns are who, whom, which, and that.
Examples:
- The person who called you is my friend.
- The book that you gave me is interesting.
Who vs. Whom
Understanding the difference between who and whom can be tricky. Here’s a simple way to remember it:
- Use who when referring to the subject of the sentence.
- Use whom when referring to the object of a verb or preposition.
Examples:
- Who is coming to the party? (Subject)
- To whom did you give the book? (Object)
Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns point to specific things. They include this, that, these, and those.
Examples:
- This is my favorite movie.
- Those are my shoes.
Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns refer to nonspecific people or things. Some common indefinite pronouns are someone, anyone, everyone, nobody, and everything.
Examples:
- Everyone is invited to the party.
- Nobody knows the answer.
Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns refer back to the subject of the sentence. They include words like myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves.
Examples:
- She taught herself to play the piano.
- I made this cake by myself.
Intensive Pronouns
Intensive pronouns are the same as reflexive pronouns, but they are used to add emphasis to the subject.
Examples:
- I myself cleaned the entire house.
- The president himself gave the speech.
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns show ownership or possession. These include mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, and theirs.
Examples:
- This book is mine.
- Is this car yours?
Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. They include who, whom, whose, which, and what.
Examples:
- Who is coming to the meeting?
- Which one do you prefer?
Reciprocal Pronouns
Reciprocal pronouns are used when two or more people are doing something to or for one another. The two reciprocal pronouns are each other and one another.
Examples:
- The two friends hugged each other.
- They help one another with homework.
Distributive Pronouns
Distributive pronouns refer to individuals within a group, considering them separately rather than collectively. These include each, either, and neither.
Examples:
- Each of the students has a book.
- Neither of the answers is correct.
Pronouns Examples
Here are a few examples of sentences using different types of pronouns:
- He gave his book to her.
- The teacher who helped me was kind.
- This is what I’ve been looking for.
- Someone left their bag on the bus.
- She looked at herself in the mirror.
- The manager himself solved the problem.
- This house is ours.
- They gave each other gifts.
- Each student must submit their assignment.
Read More